Every year, nearly 3,000 Americans die because they cannot find a matching bone marrow donor. Minorities are hit especially hard. Common sense suggests that offering modest incentives to attract more bone marrow donors would be worth pursuing, but federal law made that a felony punishable by up to five years in prison.
That is why in 2009, adults with deadly blood diseases, the parents of sick children, a California nonprofit and a world-renowned medical doctor who specializes in bone marrow research joined with the Institute for Justice to launch a legal fight against the U.S. Attorney General to put an end to a ban on offering compensation for bone marrow donors.
 The National Organ Transplant Act (NOTA) of 1984 treats compensation for marrow donors as though it were black-market organ sales. Under NOTA, giving a college student a scholarship or a new homeowner a mortgage payment for donating marrow would land everyone—doctors, nurses, donors and patients—in federal prison for up to five years.
The National Organ Transplant Act (NOTA) of 1984 treats compensation for marrow donors as though it were black-market organ sales. Under NOTA, giving a college student a scholarship or a new homeowner a mortgage payment for donating marrow would land everyone—doctors, nurses, donors and patients—in federal prison for up to five years.
NOTA’s criminal ban violated equal protection because it arbitrarily treats renewable bone marrow like nonrenewable solid organs instead of like other renewable or inexhaustible cells—such as blood—for which compensated donation is legal. That makes no sense because bone marrow, unlike organs such as kidneys, replenishes itself in just a few weeks after it is donated, leaving the donor whole once again.
In 2011, the 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals ruled in favor of the cancer patients and their attorneys from the Institute for Justice, holding that the National Organ Transplant Act’s ban on donor compensation does not apply to the most common method for donating marrow. The U.S. Attorney General sought to have that ruling overturned by the full 9th Circuit, but was unsuccessful.
The Institute for Justice’s legal victory became final in June 2012, and a new tool in the fight against deadly diseases became available, when the Attorney General declined to appeal its loss to the U.S. Supreme Court.
But no sooner was that legal victory established than the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services proposed a new rule that would negate the legal victory and block model research programs designed to examine the effectiveness of compensation. Nearly 500 people—including Nobel Laureates—wrote to HHS discouraging them from adopting the rule. But for nearly 3 years now, HHS has remained silent blocking such research and costing American cancer patients their lives.
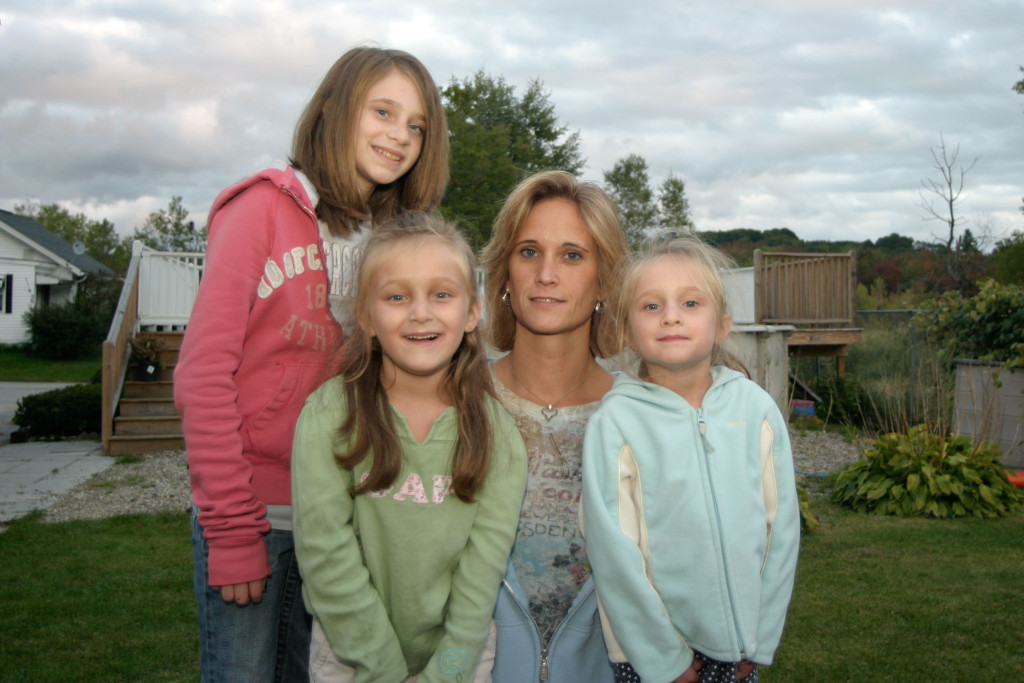 Here is a photo of Doreen Flynn and her daughters. Doreen’s real-world struggle to find bone marrow donors for her three daughters inspired the production of the movie Everything.
Here is a photo of Doreen Flynn and her daughters. Doreen’s real-world struggle to find bone marrow donors for her three daughters inspired the production of the movie Everything.